measuring time by sedimentary thickness|how to calculate sedimentation : distributing 1. Introduction. [2] Estimating erosion and deposition rates through geologic time is a foundation of geomorphology and sedimentology. Measured rates provide information about the nature and pace of landscape evolution. Resultado da 5 de jan. de 2024 · Acompanhe o sorteio da Lotofácil 2996 e confira o resultado do dia 05 de janeiro de 2024, sexta-feira, com o prêmio de hoje estimado em R$ 1.700.000,00 (um milhão e setecentos mil reais). . Avenida Paulista, 750, e o resultado da Lotofácil 2996 divulgado a partir das .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da A Bet7K é um site de apostas esportivas com a cara do Brasil! Possui saque rápido, plataforma fácil de navegar, site confiável e seguro, Suporte 24 .

We have numerous ways of measuring geological time. We can tell the relative ages of rocks (e.g., whether one rock is older than another) based on their spatial relationships, we can use . It is now recognized that the thickness of layers in sedimentary rocks can provide a valuable description of sedimentary facies and for this reason a number of size scales have .Accumulation rate has a deceptively simple formulation -- measure the thickness of the sedimentary deposit and divide by the time that elapsed between the start and finish of .
1. Introduction. [2] Estimating erosion and deposition rates through geologic time is a foundation of geomorphology and sedimentology. Measured rates provide information about the nature and pace of landscape evolution. When sedimentary processes changed to favor widespread deposition, we found that measuring time linearly systematically overestimated time duration from the resulting strata (time dilation) and misestimated the . Rate of sedimentation is essentially a ratio – an amount of sedimentation per length of time – therefore the obvious strategy to use in determining it is first to measure the amount .
Sedimentary rocks can be dated directly if they contain an igneous layer that was deposited within the sedimentary layers, like a volcanic ash. This 1-cm-thick ash bed in the uppermost Chuar Group provides a direct date of 729 ± 0.9 million . Rates of sedimentation, and stratigraphical completeness. The most obvious result of sedimentation processes is the change in the thickness of accumulated sediment with time. .
By using the H/V spectral ratio method and the modified equation that transforms resonance frequencies to sediment thickness, we generated a thickness map of the . Over time, these parent isotopes decay into stable (daughter) isotopes at a known rate. The ratio of parent to daughter isotopes in a sample changes over time. Measuring Isotope Ratios: Geologists use various analytical techniques to measure the ratio of parent to daughter isotopes in a rock or mineral. This ratio provides a way to calculate .and massive, and varying in thickness from one foot to two feet, with three feet as a rare and local maximum. The parting shales range from one to four inches in thickness, and are sharply sepa- rated from the limestone. The average thickness of the rhythmic couple, limestone and shale, is as before, eighteen inches.
sedimentation volume measurement
Geologists take great pains to measure and record geological structures because they are critically important to understanding the geological history of a region. One of the key features to measure is the orientation, or .Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock. [1] [2] [3] They form when long-term subsidence creates a regional depression that provides accommodation space for accumulation of sediments. [4]Over .Sedimentary Basins and Petroleum Systems. Richard C. Selley, Stephen A. Sonnenberg, in Elements of Petroleum Geology (Third Edition), 2015 8.1 Basic Concepts and Terms. A sedimentary basin is an area of the earth's crust that is underlain by a thick sequence of sedimentary rocks. Hydrocarbons commonly occur in sedimentary basins and are absent .Answer to How can an age for sedimentary rocks be. Skip to main content. . of individual sediment grainsMeasuring the thickness of the depositLooking at fossils in themDetermining the hardness of the rocks. How can an age for sedimentary rocks be determined? Isotopic dating of individual sediment grains. Measuring the thickness of the deposit.
Compared with normally layered or massive sediments, varved sediment sequences have several advantages for palaeoenvironmental research. They provide a basis for high-resolution studies and the possibility to calculate influx rates of any sedimentary constituent for very short and specific time intervals.PDF | On Jun 30, 2020, N.R. Abdullayev published Analysis of sedimentary thickness, volumes and geographic extent of the world sedimentary basins | Find, read and cite all the research you need on .
Thermal conductivity and diffusivity are important thermophysical rock properties, needed for heat flow determination, deep thermal regime assessment, and reconstruction of thermal history of sedimentary basins [1, 2].Thermal conductivity—k—is the heat transferred due to unit temperature gradient under steady-state conditions, through a unit area of a layer .
Along the base of the Rocky Mountains, and eastward for many miles, the basin of the Arkansas river is occupied by Cretaceous rocks. At bottom are the Dakota sandstones, several hundred feet in thickness; and above these a great body of shales, constituting the Benton, Niobrara and Pierre groups and having a total thickness of 3900 feet. In the main these shales are . The sedimentary thickness for the Oates Land coast (170–150°E) as well as the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean . and construct models that can be used to reconstruct paleobathymetry at any given geological time. The sediment thickness in the Pacific Ocean differs from the other ocean basins as it has lower average sediment thickness .Sediments and sedimentary rocks are confined to Earth’s crust, which is the thin, light outer solid skin of Earth ranging in thickness from 40–100 kilometres (25 to 62 miles) in the continental blocks to 4–10 kilometres in the ocean basins. Igneous and metamorphic rocks constitute the bulk of the crust. The total volume of sediment and sedimentary rocks can be either directly .
Bed thickness refers to the vertical measurement of a sedimentary layer, indicating how thick the layer of sediment or rock is from top to bottom. This measurement is crucial for understanding the depositional environment, as thicker beds often suggest periods of significant sediment accumulation, while thinner beds may indicate more stable conditions or slower deposition rates.a schematic column that represents the section you might measure and describe. 4.2 It turns out that in any given area, deposition is usually non-uniform in both space and time; the nature of deposition changes laterally at a given time, and it changes with time at a given point. 167
Although geologists may determine the thickness of any stratiform body of rock, most often the concern is with the thickness of layers of sedimentary rocks. In this context “measuring a section” generally refers to a lithologic description of the rock strata as well as a determination of their thicknesses (Kottlowski, 1965; Compton, 1985).of equal total sediment thickness) in the basin. lithofacies maps: for one or a series of times, draw a map showing distri-bution of sediment types being deposited at that time. ratio maps: compute things like sand/shale ratio, integrated over the entire section or restricted to some time interval, and plot a contour map of the values.
rate of sedimentation calculation
Measurement of geological features is done with a special compass that has a built-in clinometer, which is a device for measuring vertical angles. An example of how this is done is shown on Figure 12.19. Figure 12.18 A depiction of the .Photogrammetry is more time consuming and requires more equipment and skills than other methods but produces higher resolution results. . Measuring sedimentary bed thickness and geometry can be . The thickness of the sedimentary layer is varied from 0 to 3 . , with both being passive seismic approaches, is that ours is a result of a direct measurement of the sedimentary layer (the Ps b phase) . Regions of greater delay time illuminate the sedimentary basins, particularly the Cenozoic and Mesozoic basins in eastern Australia. .Question: Measuring the thickness of several sedimentary rockers would be considered blank data Measuring the thickness of several sedimentary rockers would be considered blank data Here’s the best way to solve it.
Our numerical result indicates that the sediment thickness within the Southern Benue Trough study area and parts of the Cameroon Volcanic Line vary from 0.8 to 5.5 km, with a prevailing southwest . 2.4 Estimating Sedimentary Deposit Thickness in Lowlands. To estimate the sedimentary deposit thickness in lowlands, a 30 arcsec pixel −1 grid of Topographic Ruggedness Index (TRI) [Riley et al., 1999] was first generated. TRI is the average elevation difference among a central pixel and its eight neighbors, and thus gives a measure of .Ideal: thickness of sedimentary succession across a continent, divided by rate of deposition, gives time required for deposition and thus age of Earth. Unconformity at base of sedimentary succession = time not accounted for The idea of determining Earth's age from the thickness of accumulated sedimentary rocks . . .. . . and why it fails
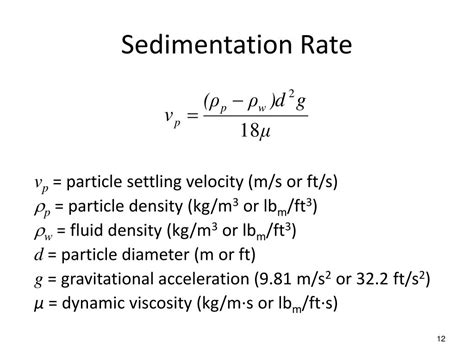
5.1 Introduction. Stratigraphy is the area of geology that deals with sedimentary rocks and layers and how they relate to geologic time; it is a significant part of historical geology. As you learned in Chapters 2 and 4, one of the primary goals of studying sedimentary rocks is to determine their depositional environment; stratigraphy is no different.As the time span of measurement lengthens, longer hiatuses tend to be incorporated into the estimated rate. Consequently, short term rates are systematically faster . Accumulation rate has a deceptively simple formulation -- measure the thickness of the sedimentary deposit and divide by the time that elapsed between the start and finish of . [1] The ejecta volume associated to a volcanic eruption is commonly estimated by extrapolating the exponential thinning relations beyond the tephra fall deposit thickness preserved in the sedimentary record. The thickness of a tephra is usually determined visually, eventually including the counting of the volcanic grains to take into account the vertical dilution .It is proposed that the beddedness of sedimentary units be expressed by the following index. Stratification index =[no. of bedsx100]/[thickness] The task of determining, measuring, and counting individual beds is large and subjective. However, it may consist of a partial sampling just as sampling for lithology or chemical composition commonly is.
water hardness test strip how to read
water hardness test strip nespresso
WEBStark Tower Defense TD is trendy, 716,092 total plays already! Play this Tower Defense game for free and prove your worth. Enjoy Stark Tower Defense TD now!
measuring time by sedimentary thickness|how to calculate sedimentation